Hemorrhoid Banding: An Effective Treatment for Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids can cause discomfort and pain, affecting many individuals. If you're experiencing symptoms such as itching, bleeding, or swelling in the anal area, hemorrhoid banding may be a suitable treatment option.
In this article, we will explore the benefits and effectiveness of hemorrhoid banding as a treatment for hemorrhoids. Understanding this procedure can help you seek appropriate medical care and find relief from the symptoms associated with hemorrhoids.
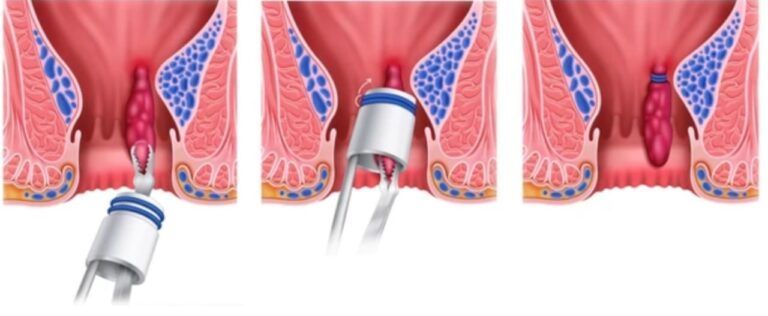
What is Hemorrhoid Banding?
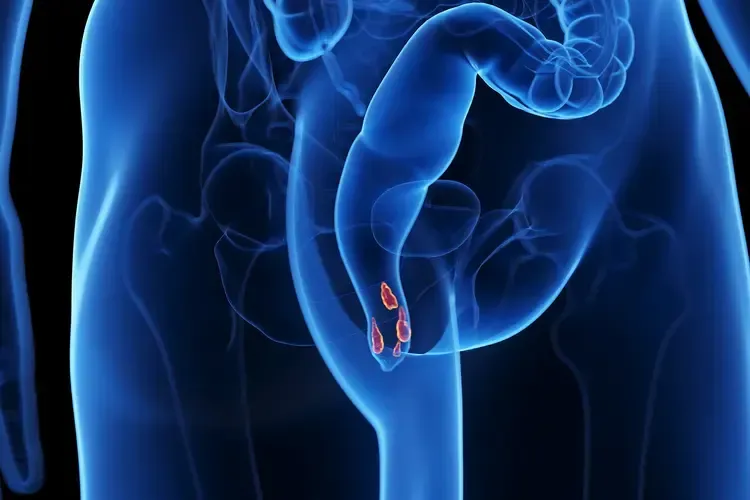
Hemorrhoid banding, also known as rubber band ligation, is a non-surgical procedure used to treat internal hemorrhoids. It involves placing small rubber bands around the base of the hemorrhoids, cutting off their blood supply. This causes the hemorrhoids to shrink and eventually fall off within a week or two.
How Does Hemorrhoid Banding Work?
During the hemorrhoid banding procedure, a gastroenterologist or a specialist inserts a special instrument called an anoscope into the rectum to visualize the hemorrhoids. They then use a device to place rubber bands around the base of the hemorrhoids, effectively cutting off their blood supply. Over time, the hemorrhoids shrink and are expelled from the body during bowel movements.
Benefits of Hemorrhoid Banding:
Hemorrhoid banding offers several benefits as a treatment option, including:
- Non-surgical approach: Hemorrhoid banding is a minimally invasive procedure that does not require incisions or anesthesia.
- Effective and long-lasting results: Rubber band ligation has been proven to be highly effective in treating internal hemorrhoids, with a success rate of approximately 80-90%.
- Quick recovery time: Most individuals can resume their normal activities within a day or two after the procedure.
- Minimal discomfort: While some mild discomfort or a feeling of pressure may be experienced during and after the procedure, it is generally well-tolerated.
Hemorrhoid Banding and Prevention of Colon Cancer:
Hemorrhoid banding can also play a role in the prevention of colon cancer. By effectively treating hemorrhoids, it reduces the risk of chronic inflammation in the anal area, which has been linked to an increased risk of developing colorectal cancer. Regular screenings, such as colonoscopies, are also important in detecting and preventing colon cancer.
In conclusion, hemorrhoid banding is an effective treatment option for individuals suffering from hemorrhoids. This non-surgical procedure offers several benefits, including long-lasting results and minimal discomfort. If you're experiencing symptoms of hemorrhoids, consult with a gastroenterologist who can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend the most suitable treatment plan for your specific situation.
Sources:
1. American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons. (2021). Hemorrhoids.
Retrieved from https://www.fascrs.org/patients/disease-condition/hemorrhoids-expanded-version
2. Mayo Clinic. (2021). Hemorrhoids. Retrieved from
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hemorrhoids/symptoms-causes/syc-20360268
3. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (2021). Hemorrhoids. Retrieved from
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/hemorrhoids