Hemorrhoids and Hemorrhoid Treatment
Hemorrhoids
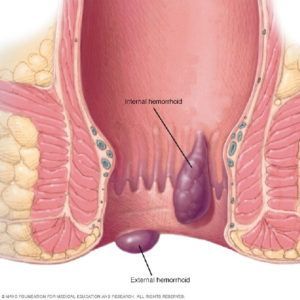
Hemorrhoids, also called piles, are swollen veins in your anus and lower rectum, similar to varicose veins. Hemorrhoids can develop inside the rectum (internal hemorrhoids) or under the skin around the anus (external hemorrhoids).
Nearly three out of four adults will have hemorrhoids from time to time. Hemorrhoids have a number of causes, but often the cause is unknown.
Fortunately, effective options are available to treat hemorrhoids. Many people get relief with home treatments and lifestyle changes.
Symptoms and Treatment
Signs and symptoms of hemorrhoids usually depend on the type of hemorrhoid. If you have been diagnosed with hemorrhoids, your doctor can discuss a hemorrhoid treatment plan with you.
External hemorrhoids
These are under the skin around your anus. Signs and symptoms might include:
- Itching or irritation in your anal region
- Pain or discomfort
- Swelling around your anus
- Bleeding
Internal hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids lie inside the rectum. You usually can’t see or feel them, and they rarely cause discomfort. But straining or irritation when passing stool can cause:
- Painless bleeding during bowel movements. You might notice small amounts of bright red blood on your toilet tissue or in the toilet.
- A hemorrhoid to push through the anal opening (prolapsed or protruding hemorrhoid), resulting in pain and irritation.
Thrombosed hemorrhoids
If blood pools in an external hemorrhoid and forms a clot (thrombus), it can result in:
- Severe pain
- Swelling
- Inflammation
- A hard lump near your anus
When to see a doctor
If you have bleeding during bowel movements or you have hemorrhoids that don’t improve after a week of home care, talk to your doctor or a gastroenterologist.
Don’t assume rectal bleeding is due to hemorrhoids, especially if you have changes in bowel habits or if your stools change in color or consistency. Rectal bleeding can occur with other diseases, including colon cancer and anal cancer.
Seek emergency care if you have large amounts of rectal bleeding, lightheadedness, dizziness or faintness.
Diagnosis
Your doctor might be able to see external hemorrhoids. Diagnosing internal hemorrhoids might include examination of your anal canal and rectum.
- Digital examination
- Your doctor inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into your rectum. He or she feels for anything unusual, such as growths.
- Visual inspection
- Because internal hemorrhoids are often too soft to be felt during a rectal exam, your doctor might examine the lower portion of your colon and rectum with an anoscope, proctoscope or sigmoidoscope.
Your doctor might want to examine your entire colon using colonoscopy if:
- Your signs and symptoms suggest you might have another digestive system disease
- You have risk factors for colorectal cancer
- You are middle-aged and haven’t had a recent colonoscopy
Treatment and Home remedies
You can often relieve the mild pain, swelling and inflammation of hemorrhoids with home treatments.
- Eat high-fiber foods. Eat more fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Doing so softens the stool and increases its bulk, which will help you avoid the straining that can worsen symptoms from existing hemorrhoids. Add fiber to your diet slowly to avoid problems with gas.
- Use topical treatments. Apply an over-the-counter hemorrhoid cream or suppository containing hydrocortisone, or use pads containing witch hazel or a numbing agent.
- Soak regularly in a warm bath or sitz bath. Soak your anal area in plain warm water for 10 to 15 minutes two to three times a day. A sitz bath fits over the toilet.
- Take oral pain relievers. You can use acetaminophen (Tylenol, others), aspirin or ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) temporarily to help relieve your discomfort.
With these treatments, hemorrhoid symptoms often go away within a week. See your doctor in a week if you don’t get relief, or sooner if you have severe pain or bleeding.
Medications
If your hemorrhoids produce only mild discomfort, your doctor might suggest over-the-counter creams, ointments, suppositories or pads. These products contain ingredients such as witch hazel, or hydrocortisone and lidocaine, which can temporarily relieve pain and itching.
Don’t use an over-the-counter steroid cream for more than a week unless directed by your doctor because it can thin your skin.
External hemorrhoid thrombectomy
If a painful blood clot (thrombosis) has formed within an external hemorrhoid, your doctor can remove the hemorrhoid, which can provide prompt relief. This procedure, done under local anesthesia, is most effective if done within 72 hours of developing a clot.
Minimally invasive procedures
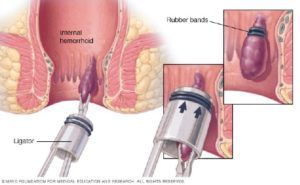
Rubber band ligation of hemorrhoidOpen pop-up dialog box
For persistent bleeding or painful hemorrhoids, your doctor might recommend one of the other minimally invasive procedures available. These treatments can be done in your doctor’s office or other outpatient setting and don’t usually require anesthesia.
- Rubber band ligation. Your doctor places one or two tiny rubber bands around the base of an internal hemorrhoid to cut off its circulation. The hemorrhoid withers and falls off within a week.
Hemorrhoid banding can be uncomfortable and cause bleeding, which might begin two to four days after the procedure but is rarely severe. Occasionally, more-serious complications can occur.
- Injection (sclerotherapy). Your doctor injects a chemical solution into the hemorrhoid tissue to shrink it. While the injection causes little or no pain, it might be less effective than rubber band ligation.
- Coagulation (infrared, laser or bipolar). Coagulation techniques use laser or infrared light or heat. They cause small, bleeding internal hemorrhoids to harden and shrivel. Coagulation has few side effects and usually causes little discomfort.
Surgical procedures
Only a small percentage of people with hemorrhoids require surgery. However, if other procedures haven’t been successful or you have large hemorrhoids, your doctor might recommend one of the following:
- Hemorrhoid removal (hemorrhoidectomy). Choosing one of various techniques, your surgeon removes excessive tissue that causes bleeding. The surgery can be done with local anesthesia combined with sedation, spinal anesthesia or general anesthesia.
Hemorrhoidectomy is the most effective and complete way to treat severe or recurring hemorrhoids. Complications can include temporary difficulty emptying your bladder, which can result in urinary tract infections. This complication occurs mainly after spinal anesthesia.
Most people have some pain after the procedure, which medications can relieve. Soaking in a warm bath also might help.
- Hemorrhoid stapling. This procedure, called stapled hemorrhoidopexy, blocks blood flow to hemorrhoidal tissue. It is typically used only for internal hemorrhoids.
Stapling generally involves less pain than hemorrhoidectomy and allows for earlier return to regular activities. Compared with hemorrhoidectomy, however, stapling has been associated with a greater risk of recurrence and rectal prolapse, in which part of the rectum protrudes from the anus.
Complications can also include bleeding, urinary retention and pain, as well as, rarely, a life-threatening blood infection (sepsis). Talk with your doctor about the best option for you.
Source : Mayo Clinic.
Read More About Hemorrhoids Diagnosis and treatment
Learn About Thrombosed Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids Diagnosis and treatment
Symptoms of hemorrhoids that you must identify
The post Hemorrhoids and Hemorrhoid Treatment appeared first on Gastro SB.