What are hemorrhoids?
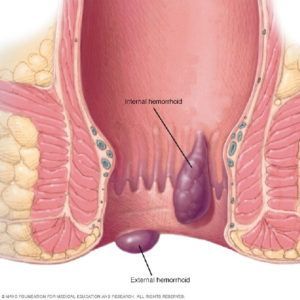
Hemorrhoids are when the veins or blood vessels in and around your anus and lower rectum become swollen and irritated. This happens when there is extra pressure on these veins.
Hemorrhoids can be either inside your anus (internal) or under the skin around your anus (external).
Hemorrhoids are very common in both men and women. About half of all people will have hemorrhoids by age 50.
Many women get hemorrhoids during pregnancy and childbirth. The pressure of carrying a baby in your belly puts extra stress on the blood vessels in your pelvic area. Straining to push the baby out when giving birth also puts extra pressure on these blood vessels.
What causes hemorrhoids?
You may get hemorrhoids if you:
- Often strain during bowel movements
- Are pregnant
- Have a family history of hemorrhoids
- Are older
- Have long-term or chronic constipation or diarrhea
Who is at risk for hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids are very common. Most people will have a hemorrhoid at some time in their life.
You are more likely to get hemorrhoids if you:
- Are pregnant
- Sit on the toilet for too long
- Are obese
- Do things that make you strain more, such as heavy lifting
- Have a family history of hemorrhoids
- Have long-term or chronic constipation or diarrhea
- Are between 45 and 65 years old
What are the symptoms of hemorrhoids?
Each person’s symptoms may vary. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Bright red blood in your stool, on toilet paper, or in your toilet bowl
- Pain and irritation around your anus
- Swelling or a hard lump around your anus
- Itching
Hemorrhoid symptoms may look like other health problems. Always see your healthcare provider to be sure.
How are hemorrhoids diagnosed?
Having blood in your stool can also be a sign of other digestive disorders, such as colorectal cancer. It’s important to see your healthcare provider for a complete exam.
To see if you have hemorrhoids, your healthcare provider may do several tests including:
- Physical exam. This is done to check your anus and rectum and look for swollen blood vessels that are a sign of hemorrhoids.
- Digital rectum examination (DRE). Your healthcare provider inserts a gloved, greased (lubricated) finger into your rectum to check for any problems.
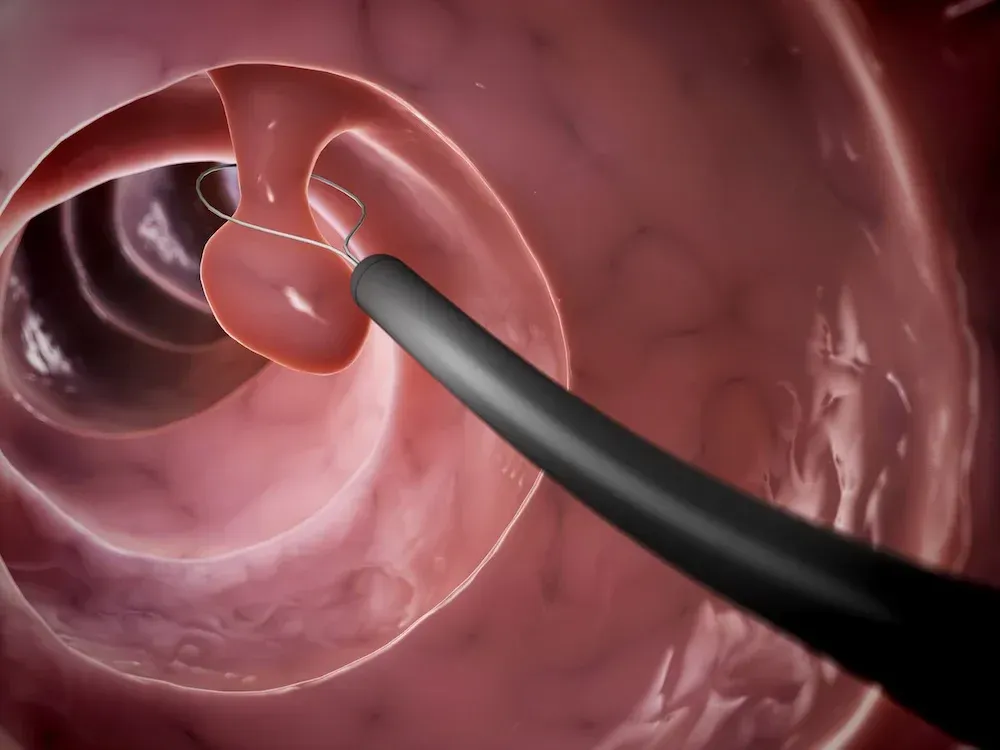
- Anoscopy. A hollow, lighted tube is put into your anus. This is used to see internal hemorrhoids.
- Proctoscopy. A lighted tube is put into your anus. This gives a view of your entire rectum.
- Sigmoidoscopy. This test checks the inside of part of your large intestine. It helps to tell what is causing diarrhea, belly pain, constipation, abnormal growths, and bleeding. A short, flexible, lighted tube (sigmoidoscope) is put into your intestine through the rectum. This tube blows air into your intestine to make it swell. This makes it easier to see inside. A tissue sample (biopsy) can be taken if needed.
- Colonoscopy. This test looks at the full length of your large intestine. It can help check for any abnormal growths, tissue that is red or swollen, sores (ulcers), or bleeding. A long, flexible, lighted tube called a colonoscope is put into your rectum up into the colon. This tube lets your healthcare provider see the lining of your colon and take out a tissue sample (biopsy) to test it. He or she may also be able to treat some problems that may be found.
How are hemorrhoids treated?
Your healthcare provider will create a care plan for you based on:
- Your age, overall health, and past health
- How serious your case is
- Whether you have internal hemorrhoids, external hemorrhoids, or both
- How well you handle certain medicines, treatments, or therapies
- If your condition is expected to get worse
- What you would like to do
The main goal of treatment is to reduce your symptoms. This may be done by:
- Sitting in plain, warm water in a bathtub several times a day
- Using ice packs to reduce swelling
- Using hemorrhoid creams or medicines inserted into your rectum (suppositories)
Your healthcare provider may also suggest that you add more fiber and fluids to your diet to help soften your stools. Having softer stools means you don’t have to strain during bowel movements. This reduces the pressure on your hemorrhoids.
Adding more fiber to your diet means eating more:
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Whole grains
Your healthcare provider may also suggest that you take stool softeners or fiber supplements.
In some cases, surgery is needed. There are several types of surgeries used to remove or reduce internal and external hemorrhoids. These include:
- Rubber band ligation. A rubber band is placed around the base of the hemorrhoid inside your rectum to cut off circulation to the hemorrhoid. The hemorrhoid shrinks and goes away in a few days.
- Sclerotherapy. A chemical solution is shot (injected) around the blood vessel to shrink the hemorrhoid.
- Electrical coagulation, also called infrared photo coagulation. A special device uses a beam of infrared light to burn hemorrhoid tissue.
- Hemorrhoidectomy and hemorrhoidopexy. These procedures permanently remove your hemorrhoids.
What are the complications of hemorrhoids?
In rare cases, hemorrhoids may cause other problems. These may include:
- Having a low blood count that makes you tired (anemia). This can happen because of bleeding from a long-term or chronic hemorrhoid.
- Blood flow being cut off from a hemorrhoid that is sticking out (prolapsed). This can happen when the blood supply to the hemorrhoid is cut off. This can be very painful and cause bleeding. You may need surgery.
What can I do to prevent hemorrhoids?
It’s not always possible to stop hemorrhoids from happening. But you may reduce your risk of getting hemorrhoids if you:
- Eat a healthy diet, with plenty of fiber and liquids
- Limit the amount of time you sit on the toilet
- Work with your healthcare provider to manage constipation and prevent straining
- Stay at a healthy weight
When should I call my healthcare provider?
Call your healthcare provider if your symptoms get worse or if you have new symptoms. Also call if you see blood in your stool or on toilet paper for the first time, or if you see more blood than normal.
Key points about hemorrhoids
- Hemorrhoids are a swelling of the veins or blood vessels in and around your anus and lower rectum. This happens when there is extra pressure on these veins.
- Hemorrhoids are either inside your anus (internal) or under the skin around your anus (external).
- About half of all people will have hemorrhoids by age 50.
- Many women get hemorrhoids during pregnancy and childbirth.
- You may get hemorrhoids if you have a family history, often strain during bowel movements, or have long-term (chronic) constipation or diarrhea.
- Symptoms may include blood in your stool, pain around your anus, or itching.
- Your healthcare provider may do several tests to be sure you have hemorrhoids.
- You may need to add more fiber and fluids to your diet.
- The goal of treatment is to reduce your symptoms.
- In some cases, surgery is needed.
Source: John Hopkins Medicine.
The post What are hemorrhoids? appeared first on Gastro SB.