Obesity in Adults: Overview of Management & Procedures for Weight Loss

The medical rationale for weight loss is that obesity is a serious, chronic, and progressive disease and is associated with a significant increase in mortality and many health risks including type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and coronary heart disease. The benefits of procedures for weight loss include a reduction in the rate of progression from impaired glucose tolerance to diabetes, blood pressure in hypertensive patients, and lipid levels in higher risk patients. Other non-cardiac benefits of weight loss include reductions in urinary incontinence, sleep apnea, and depression, as well as improvements in quality of life, physical functioning, and mobility.
Selection of treatment for people with overweight or obesity is based upon an initial risk assessment.
All patients who would benefit from weight loss should receive counseling on diet, exercise, and goals for weight management from a weight loss clinic or weight loss coach.
Candidates for pharmacologic therapy include adults with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 30 kg/m2, or a BMI of 27 to 29.9 kg/m2 with comorbidities, who have not met weight loss goals (loss of at least 5 percent of total body weight at three to six months) with a comprehensive lifestyle intervention. The decision to initiate drug therapy should be individualized and made after a careful evaluation of the risks and benefits of all treatment options (lifestyle, pharmacologic, surgical).
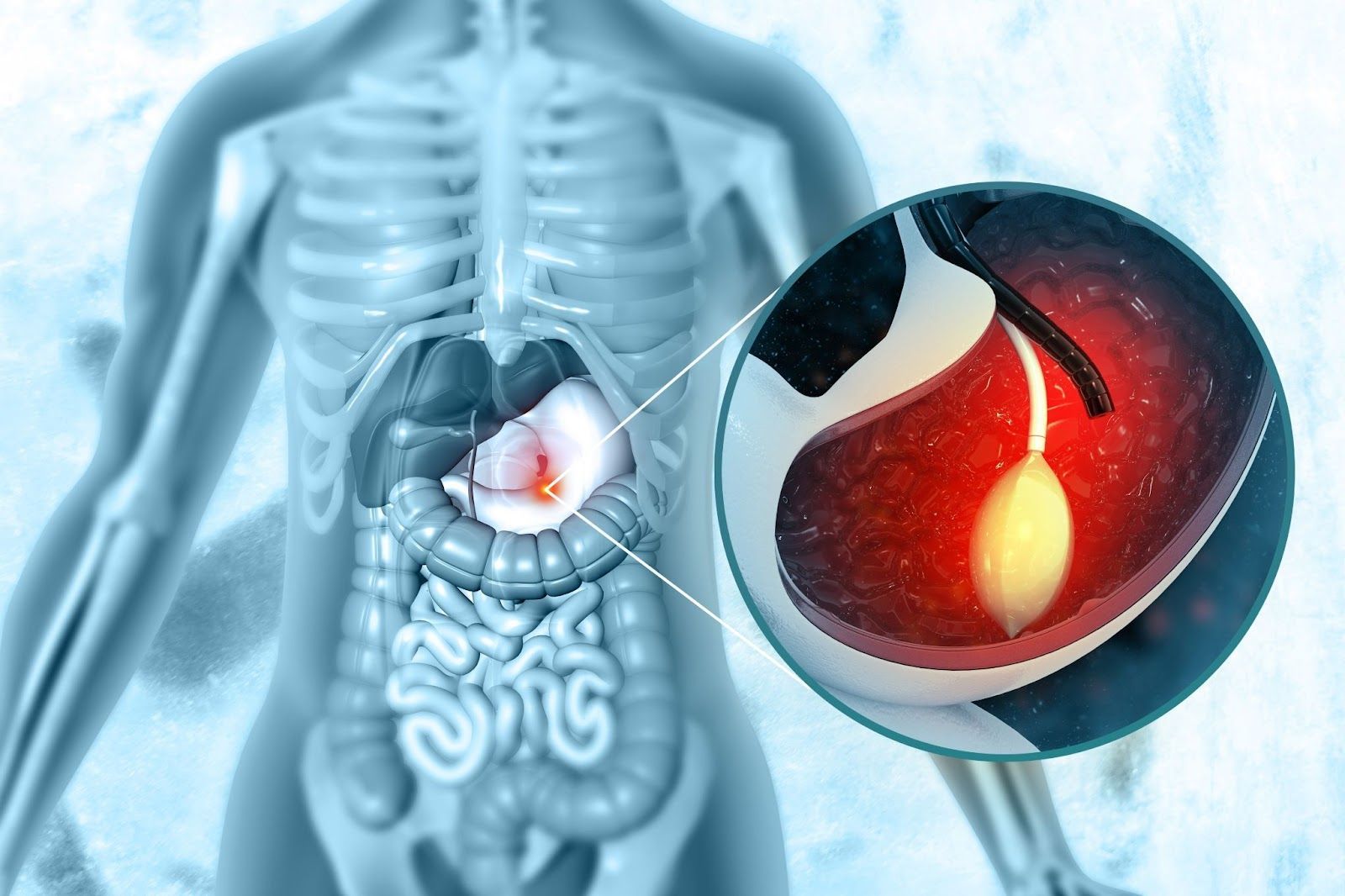
There are several types of devices approved for use in the treatment of obesity like the gastric balloon. The use of one of these devices may be considered for use in those patients in whom medications are ineffective or not tolerated, for those patients who are unable or unwilling to undergo bariatric surgery, or as a bridging therapy prior to bariatric surgery. In referring a patient to receive one of these devices, it is important to note that the BMI indication for each device is different, with a BMI range between 25 to 55 kg/m2.
Candidates for bariatric surgery include adolescents and adults with a BMI ≥40 kg/m2, or a BMI of 35 to 39.9 kg/m2 with at least one serious comorbidity, who have not met weight loss goals with diet, exercise, and drug therapy.
Consumption of a reduced calorie diet, frequent self-weighing, and participation in a lifestyle intervention program are strategies to help maintain weight loss. However, the body appears to have a “set point” of adipose tissue mass, and strategies that assume the effective treatment of obesity is only a matter of an individual’s “willpower” may lead to repeated failure due to the body’s tendency to revert to its set point. Bariatric surgery, which may alter the body’s adipose tissue set point, and extended use of anti-obesity pharmacologic therapy may help address these underlying physiologic changes.
Source : Uptodate ®
Learn More About Diet And Medication For Weight Loss
Patient Education: Procedures for Weight Loss (The Basics)
Patient Education: Procedures for Weight Loss & Surgery (Beyond the Basics)
Procedures for Weight Loss . . . WE’RE IN IT TOGETHER
Obesity in Adults: Behavioral Therapy & Weight Loss Clinics
Patient Education: Health Risks of Obesity & Weight Loss Tips (The Basics)
Gastro SB Weight Loss Clinic: Medications Used for Weight Loss
Dietary Assessment And Weight Loss
The Ultimate Guide for Plant Based Weight Loss
Weight Loss Medications Explained
The post Obesity in Adults: Overview of Management & Procedures for Weight Loss appeared first on Gastro SB.